 Kit Houses
Kit Houses
National 3
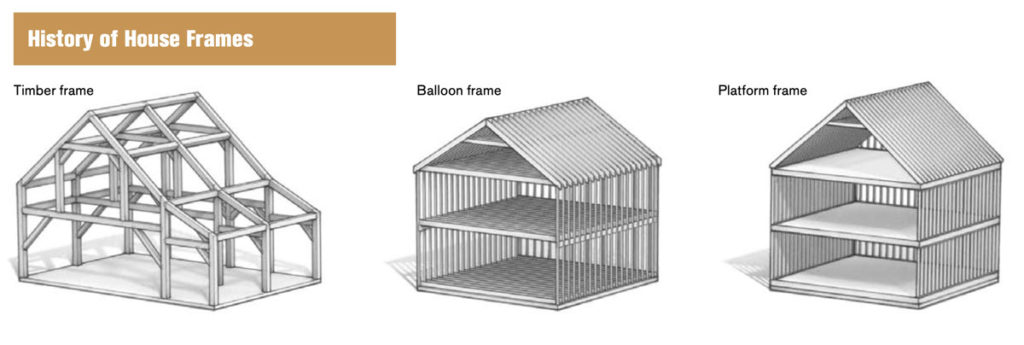
The dizzying array of house models offered by kit house companies was made possible by advances in wood-frame construction. In the mid-nineteenth century, timber frame construction yielded to balloon frame construction, and by the 1930s, platform framing—both of which used dimensional lumber and nails rather than heavy timbers and joinery. This allowed a more complex design with a flexible floor plan and required less skill to erect.
In the early decades of the twentieth century, Tudor, Colonial Revival, and Victorian styles were popular, as well as more modest bungalows, Foursquares, Capes, and cottages. Kit houses offered versions of these styles, often “borrowing” from architect plan books and each other.


To feed consumer hunger for housing, financial institutions began to offer credit backed by Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loan guarantees—placing ownership of a house within reach of average Americans. The establishment of the Federal Housing Administration in 1934 under the New Deal was designed to combat the devastation of the Great Depression by increasing housing stock and home ownership.